China launched its 16th satellite of its satellite positioning system BeiDou-2. Like all other Chinese satellites, it was put into orbit by their own rocket Long March 3.
China launched its 16th satellite of its satellite positioning system BeiDou-2. Like all other Chinese satellites, it was put into orbit by their own rocket Long March 3.
It is the sixth satellite launched this year to complete the constellation of satellites that will make up the BeiDou-2 navigation network. Started in 2007, this network is the successor to the BeiDou-1 project launched in October 2000 and gradually made up of 4 Experimental satellites.
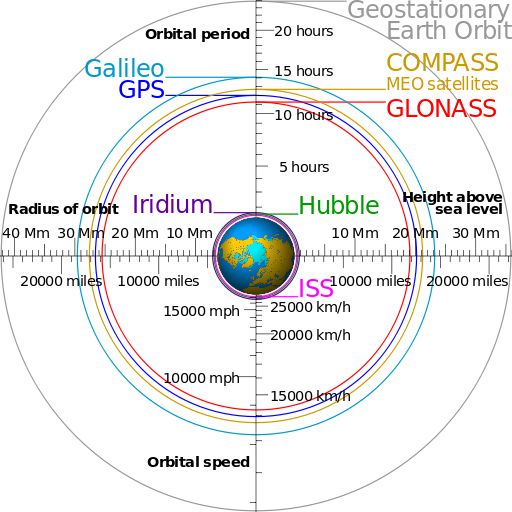
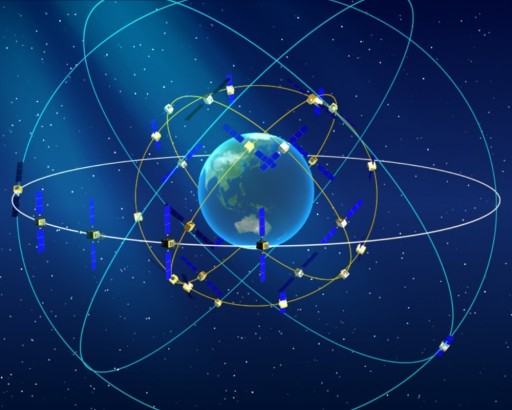 This new system will eventually consist of 35 satellites, Including 5 Satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO*) and 30 Medium-Earth orbit satellites (MEO*). It should start to provide satellite positioning for a major part of the Asia-Pacific region in early 2013. The network should be able to provide global services by 2020.
This new system will eventually consist of 35 satellites, Including 5 Satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO*) and 30 Medium-Earth orbit satellites (MEO*). It should start to provide satellite positioning for a major part of the Asia-Pacific region in early 2013. The network should be able to provide global services by 2020.
The official website of the Chinese People's Army said that BeiDou is becoming a major provider of satellite navigation services for the entire world, as well as other systems including the U.S. GPS, Russian GLONASS and the European Galileo system. BeiDou-2 has been designed to be compatible and work in conjunction with GPS and GLONASS (**).
Like its competitors, BeiDou-2 will be used for many civil and military applications. The potential of users in China is estimated by official institutes to be 95% population. The director of the Institute of Earth and Space Information said : "As soon as civil services are marketed, BeiDou will be able to replace the American GPS. When it comes to matters of national security, reliance on GPS can be reduced, or even eliminated". However, it is more likely that the two systems will be used in parallel.
Will note that, after commercial commissioning GLONASS by the Russians in autumn 2011, then BeiDou-2 beginning 2013, Europeans have fallen behind in the global race for independence in this strategic area with GALILEO which should not be operational before the end 2014. Provided that Europe's economic situation improves…
—
(*) Orbits used for satellites : GEO (Geostationary Earth Orbit) at 35786 km high, MEO (Medium Earth Orbit) from 2000 and 35786 km, LEO (Low Earth Orbit) from 160 and 2000 km high :
(**) Themselves compatible with Galileo : same WGS84 datum and same frequencies allowing receivers to either receive signals from all these networks.
—